Latest Advances in ai in 2025
In 2024 and early 2025, the field of artificial intelligence (AI) achieved remarkable progress, with its impact spanning across various industries. AI models demonstrated significant performance improvements in multiple benchmarks, marking a new level of capability in handling complex tasks [1]. From healthcare to transportation, AI is integrating into daily life at an unprecedented pace [1]. Business adoption and investment in AI also showed strong growth, particularly in generative AI [1]. The United States maintained its lead in AI model development, but China is rapidly closing the quality gap [1]. Meanwhile, the responsible AI ecosystem continues to evolve, with increasing attention to ethical considerations and regulation [1]. Global optimism about AI has risen overall, though regional differences persist [1].
Major Technological Breakthroughs
Advancements in AI capabilities have been driven by a series of core technological breakthroughs.
Performance Improvements in Key Benchmarks
Rigorous evaluations of AI system performance revealed substantial progress across several challenging benchmarks [1].
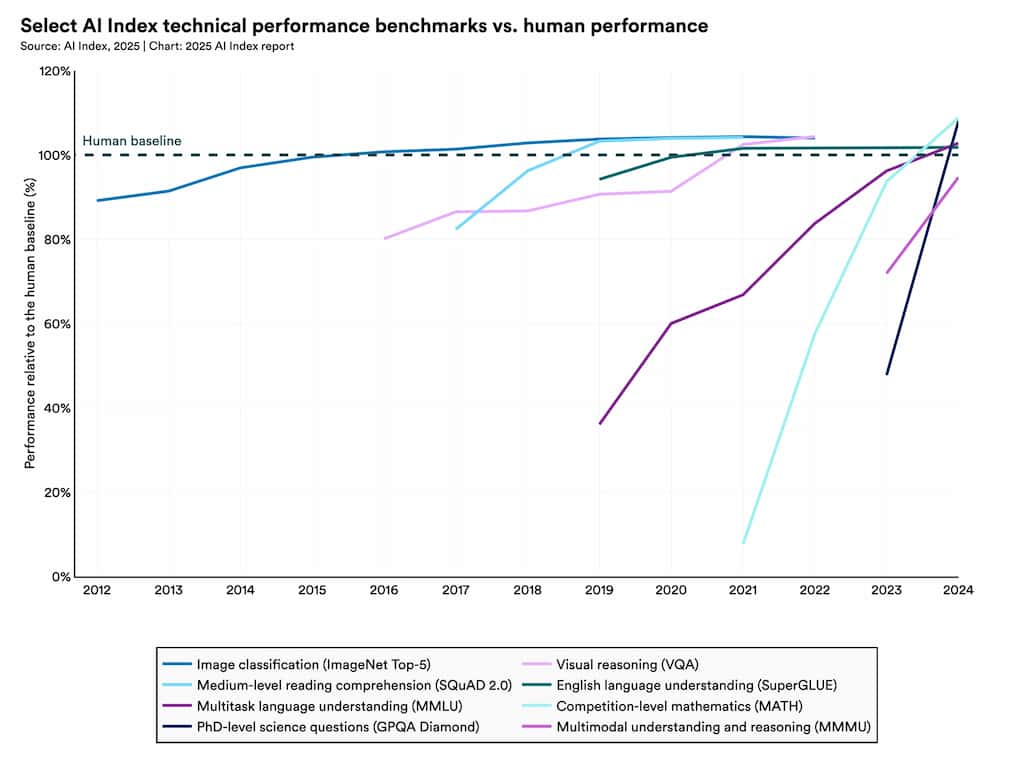
Benchmarks such as MMMU, GPQA, and SWE-bench were introduced in 2023 to test the limits of advanced AI systems. Just one year later, in 2024, these benchmarks saw dramatic performance improvements [1].
Specifically, MMMU scores increased by 18.8 percentage points, GPQA by 48.9 percentage points, and SWE-bench by a staggering 67.3 percentage points [1]. The leap in SWE-bench is particularly noteworthy, indicating rapid progress in complex and nuanced fields like software development.
These improvements are not merely numerical gains—they signal AI's shift from pattern recognition toward more robust problem-solving capabilities.
The introduction of these benchmarks in 2023 set a high standard for measuring AI performance, and the significant progress achieved within just one year reflects the accelerating pace of core AI algorithm and architectural innovation.
These benchmarks cover diverse areas such as mathematical reasoning (MMMU), general knowledge (GPQA), and software development (SWE-bench), suggesting that performance gains are not confined to niche domains but reflect broader advancements in AI intelligence.
Beyond benchmark improvements, AI systems have also made significant strides in generating high-quality video [1].
Additionally, in certain cases, language model agents have surpassed human performance in programming tasks within limited time constraints [1].
These advancements, combined with benchmark progress, demonstrate that AI models are becoming increasingly sophisticated and versatile, capable of excelling in both creative and highly technical domains.
Outperforming humans in programming tasks under time constraints suggests AI's potential to significantly augment or even automate certain aspects of software development workflows.
The ability to generate high-quality video reflects progress in understanding and modeling complex visual information.
Superior performance in programming tasks highlights AI's growing proficiency in logical reasoning and code generation, hinting at potential transformations in how software is created and maintained.
Advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs)
Large language models have been a key driver of recent AI progress, evolving at a rapid pace.
The context window length of long-context LLMs has expanded dramatically, growing from an initial 8K tokens to 128K and even 1M tokens [6]. This expansion enables LLMs to process and comprehend longer documents and conversations, leading to notable improvements in tasks such as summarizing lengthy reports, answering questions based on entire books, and analyzing multi-chapter documents. This marks a shift toward AI systems capable of handling more complex and context-dependent information.
The ability to process longer contexts directly addresses a key limitation of earlier LLMs. By retaining more information, these models can generate more coherent and relevant responses, opening new possibilities for applications like research, content analysis, and complex problem-solving.
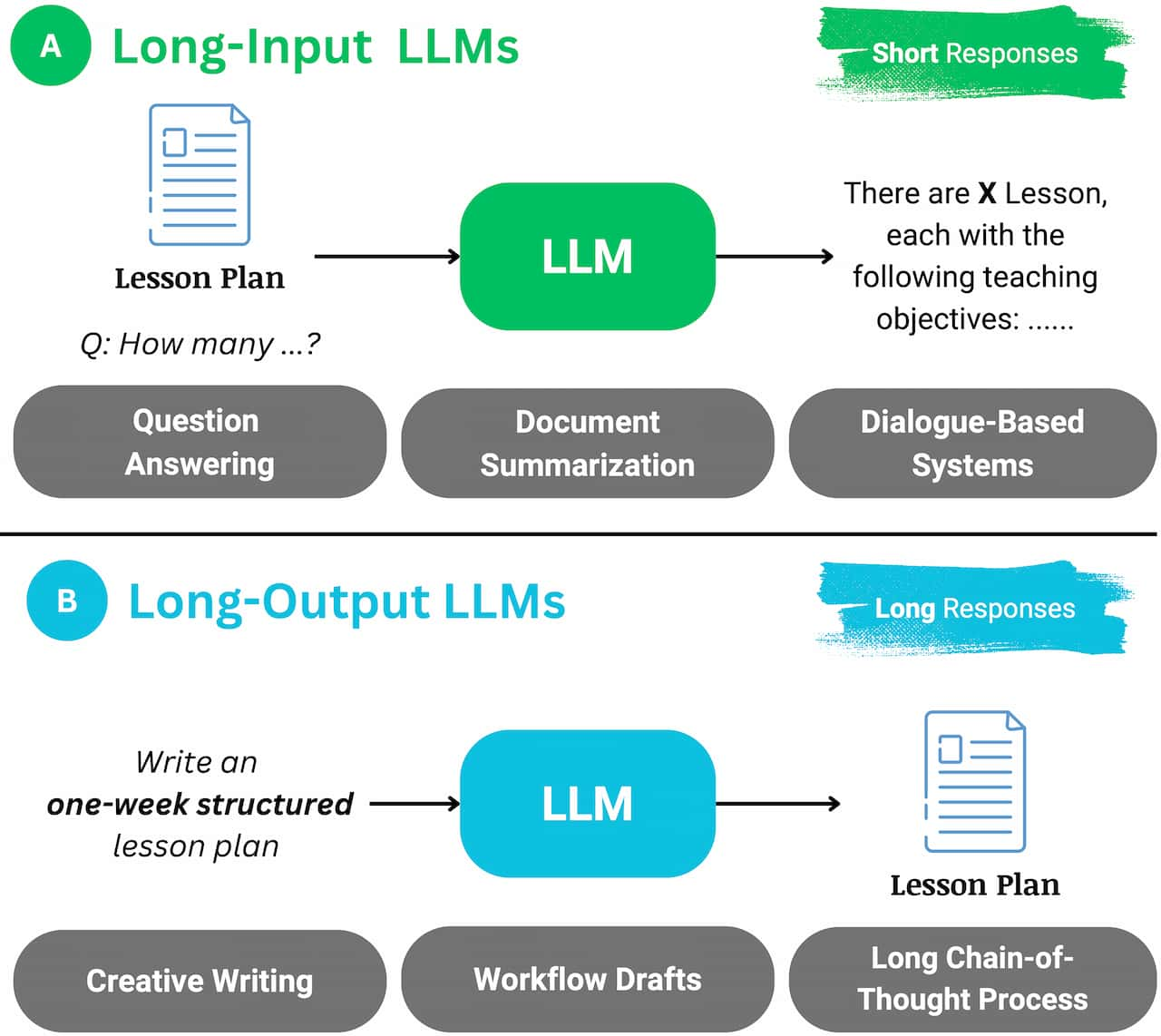
Research has also focused on improving LLMs' ability to generate long-form outputs, an area that has received relatively less attention compared to long-context understanding [6]. Addressing challenges in long-output generation is critical for applications like novel writing, long-term planning, and complex reasoning, where models must produce lengthy, coherent, and contextually rich text.
This indicates a maturation of LLM research toward more sophisticated content creation capabilities. While understanding long inputs is important, generating lengthy, coherent, and relevant outputs is equally vital for many practical applications. Targeted research in this area reflects a recognition of this need and efforts to further expand LLM capabilities.
Progress in Generative AI
AI models have also made significant strides in generating new content.
Google released Gemini 2.0, designed for the "Agent Era," featuring capabilities like Deep Research and improved speed and efficiency in models such as Gemini 2.0 Flash [7].
Imagen 3, Google's highest-quality text-to-image model, was also released, offering enhanced detail and realism [7].
Google's video generation model, Veo 2, demonstrates improved understanding of real-world physics and the nuances of human motion [7]. Additionally, Google's text-to-audio tool, MusicFX, has been updated with features like MusicFX DJ for real-time music creation [7].
Google's continuous advancements in generative AI models across text, image, video, and audio highlight the rapid evolution of AI's creative capabilities.
The focus on "Agent Era" models like Gemini 2.0 signals a shift toward AI that can actively assist users with complex tasks. Synchronized improvements across multiple modalities indicate comprehensive progress in generative AI technology.
Features like Deep Research in Gemini mark AI's transition from simple content generation to more intelligent and autonomous assistance.
Advances in AI Agents
The emergence and growing capabilities of autonomous AI systems represent a significant trend in the field.
By 2025, AI agents are expected to perform more tasks with greater autonomy, even acting on behalf of users [8].
Agent AI—where AI programs collaborate to accomplish real-world tasks—is a major trend for 2025, with many anticipating increased investment in this area [4].
OpenAI introduced Deep Research in ChatGPT, an agent feature capable of conducting multi-step online research to complete complex tasks [9].
The growing emphasis on AI agents suggests that AI systems are becoming more independent and proactive, capable of automating complex workflows and providing more comprehensive assistance to users.
This trend has the potential to significantly enhance productivity and transform how humans interact with technology. The evolution of AI agents from simple tools to autonomous assistants represents a critical step in AI's progression.
Their ability to handle multi-step tasks and collaborate hints at a future where AI plays a more prominent and active role in work and daily life.
Improvements in Smaller, More Efficient Models
The development of smaller, more efficient AI models is another important trend.
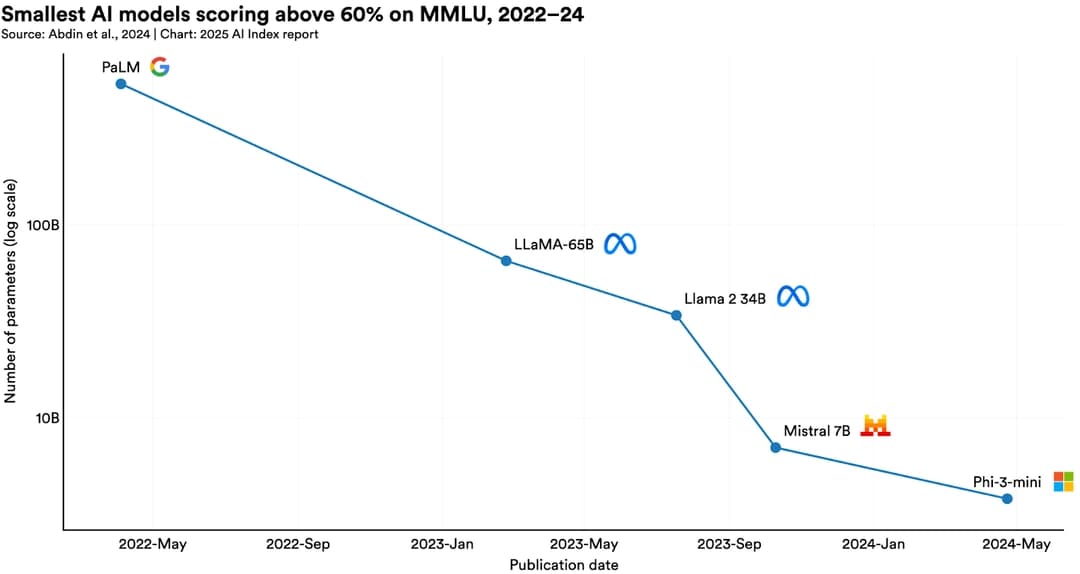
Models like Microsoft's Phi-3-mini achieve performance comparable to larger models from 2022 but with far fewer parameters [2].
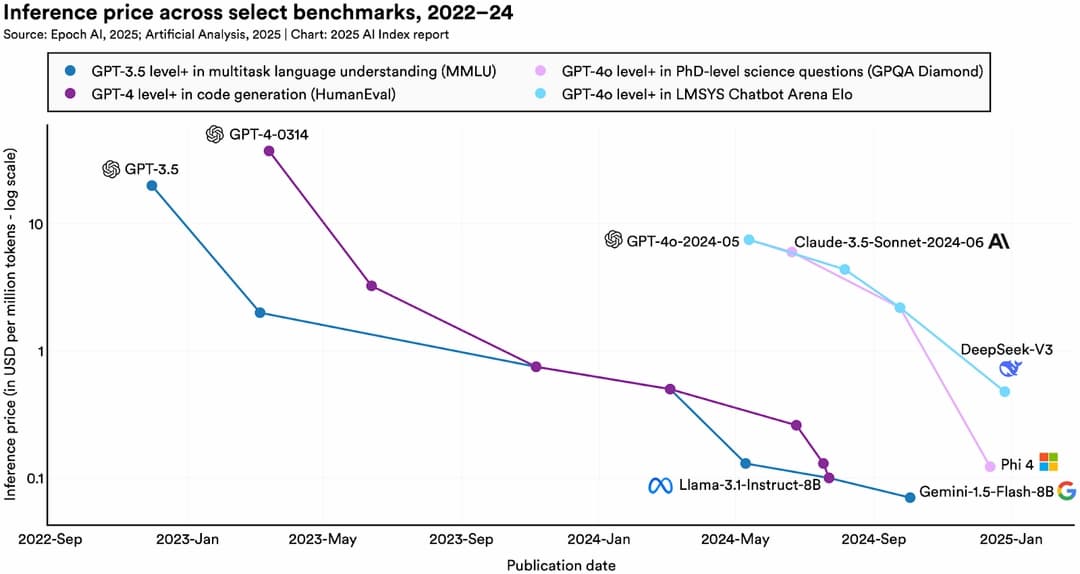
In 2024, the cost of querying GPT-3.5-level AI models dropped significantly, reflecting improved efficiency [2].
The cost per million tokens for querying an AI model with performance equivalent to GPT-3.5 (64.8% accuracy on MMLU) fell from $20 in November 2022 to $0.07 in October 2024 (Gemini-1.5-Flash-8B)—a reduction of over 280x in roughly 18 months.
Depending on the task, LLM inference prices have decreased by 9x to 900x annually.
Open-weight models are rapidly closing the performance gap with closed models, becoming more accessible and easier to use [2]. This trend toward smaller, more efficient, and increasingly capable open-weight models is making advanced AI more widely available for diverse applications and users, including deployment on resource-constrained devices.
Achieving high performance with smaller models reduces the computational resources required for training and inference, lowering costs and energy consumption. The rise of open-weight models fosters innovation and collaboration within the AI community.
Widespread AI Adoption Across Industries
AI is being increasingly adopted across industries, driving significant transformation.
AI in Healthcare
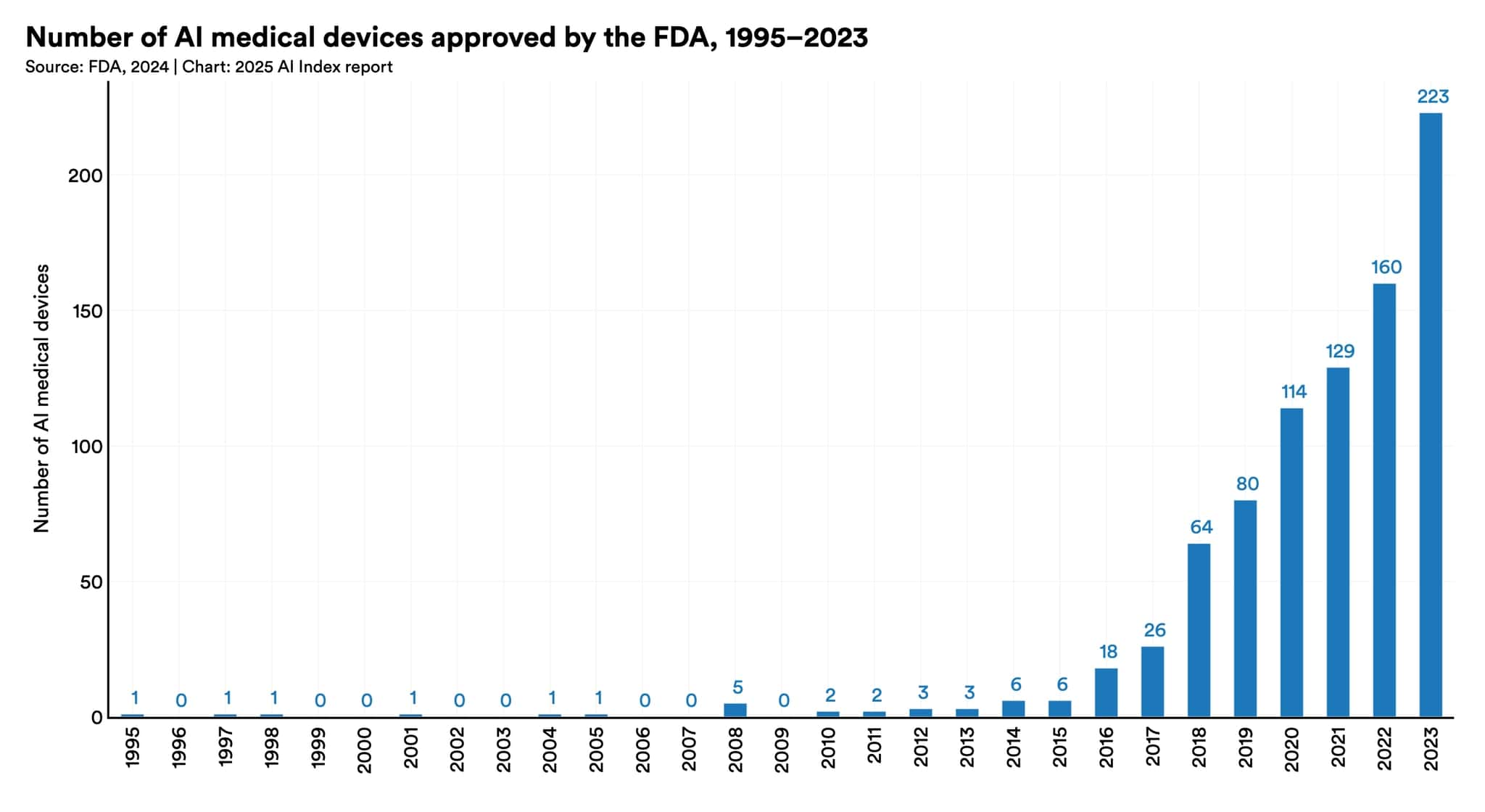
AI usage in healthcare is growing. The number of FDA-approved AI medical devices rose notably in 2023 compared to previous years, indicating deeper integration of AI in healthcare [1].
AI is accelerating drug discovery and improving patient care, enabling more personalized and effective treatments [12].
AI systems are also being used to predict protein structures and design novel protein binders, aiding drug discovery and biosensor development [7].
The increasing number of FDA-approved AI medical devices reflects growing trust and acceptance of AI in clinical applications.
AI's role in accelerating drug discovery and personalized treatments suggests transformative potential for healthcare research and patient outcomes.
The FDA's rigorous approval process indicates that AI in healthcare is moving from theoretical applications to real-world deployment.
AI's ability to analyze complex biological data and design new molecules could revolutionize the pharmaceutical industry.
AI in Transportation
Autonomous vehicles are transitioning from experimentation to public use, with companies like Waymo and Baidu operating large fleets of self-driving taxis [1].

AI is optimizing supply chain management for logistics companies, improving efficiency [12].
Elon Musk announced plans to launch a "RoboTaxi" service by June 2025, featuring cars without steering wheels [15].

The growing prevalence of autonomous taxis and AI applications in logistics underscores the increasing maturity and real-world impact of AI in transportation.
This trend has the potential to reshape urban mobility and supply chain efficiency. The shift from pilot projects to widespread public use of autonomous vehicles reflects significant progress in reliability and safety.
AI's role in logistics highlights its ability to optimize complex systems and enhance operational efficiency.
AI in Business and Finance
In 2024, the vast majority of organizations reported using AI in their operations, a significant increase over the previous year [1].
Generative AI is being used to streamline workflows, automate tasks, and enhance productivity across various business functions [4].
AI is also seeing broader adoption in finance, including fraud detection, risk assessment, personalized banking experiences, and algorithmic trading [12]. The widespread use of AI in business and finance highlights its value in improving efficiency, enhancing customer experiences, and driving innovation.
Specific applications in finance demonstrate AI's ability to analyze complex financial data and automate critical processes. High adoption rates indicate that AI is no longer a niche technology but a core component of modern business operations.
The diverse applications of AI in the highly regulated and data-intensive finance industry attest to its versatility and potential for significant impact.
AI in Education
AI is enabling personalized learning experiences tailored to each student's unique needs and pace [12]. AI-powered intelligent tutoring systems provide students with individualized guidance and feedback [25].

AI tools are also being used to automate grading and feedback, reducing the administrative burden on educators [25]. AI's ability to personalize learning and automate tasks has the potential to revolutionize education, making it more engaging, effective, and accessible.
Intelligent tutoring systems offer tailored support, while automated grading frees educators to focus on more strategic aspects of teaching.
The emphasis on personalized learning addresses diverse student needs and can improve learning outcomes. Automating administrative tasks allows educators to dedicate more time to student interaction and curriculum development.
AI in Software Engineering
AI-driven code completion is becoming increasingly popular and effective, with a significant portion of Google's internal code now being AI-assisted [5].

AI is also being used to address code review feedback and automatically adapt pasted code, further streamlining the development process [28]. Advances in AI-assisted software engineering suggest a future where AI plays a greater role in coding, potentially boosting developer productivity and code quality.
The integration of AI into development workflows reflects the growing maturity of these tools. The high adoption of AI-driven code completion at major tech companies like Google demonstrates its practical value. AI's application in code reviews and adaptations further underscores its potential to automate various stages of the software development lifecycle.
Recently, OpenAI announced the acquisition of AI programming assistant startup Windsurf for $3 billion. Windsurf has attracted over 800,000 developer users and serves around 1,000 enterprise customers, with annual recurring revenue growing from $40 million in February 2025 to approximately $100 million.
The Global AI Landscape
AI development and adoption exhibit complex international dynamics.
U.S. vs. China in AI Development
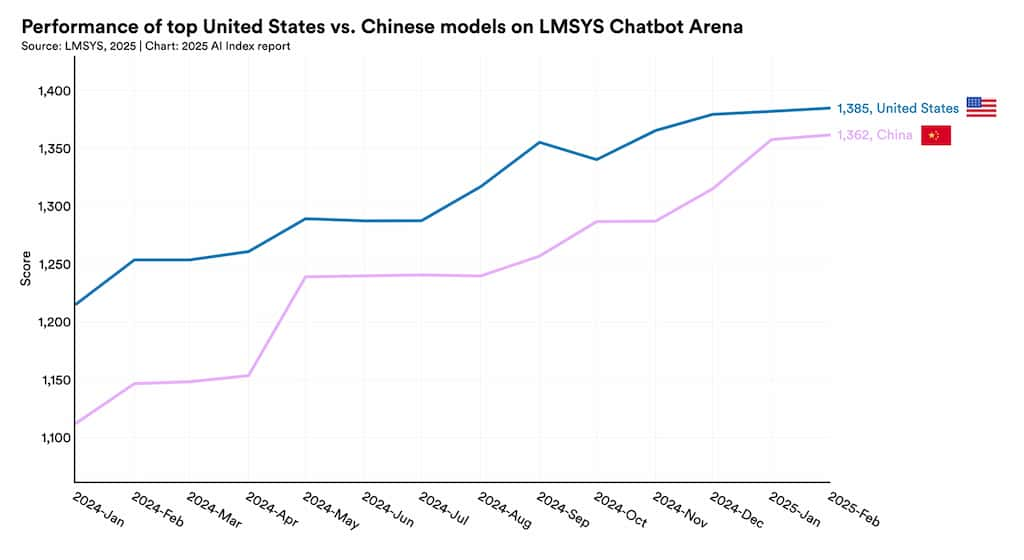
The U.S. led in the number of notable AI models produced in 2024, but China is rapidly closing the quality gap [1].

China continues to lead in AI publications and patents, reflecting its strong emphasis on foundational research [1]. In 2024, private AI investment in the U.S. far exceeded that in China [1]. While the U.S. currently leads in top-tier AI model output and private investment, China's rapid progress in model quality and continued dominance in research output suggest a highly competitive global landscape.
The differing strengths of the two countries hint at potential divergences in future AI development and deployment trajectories. The U.S.'s advantage in model development and investment may translate into faster commercialization, while China's research focus could yield foundational breakthroughs.
The narrowing quality gap indicates China's rapid catch-up in AI capabilities.
Global AI and Generative AI Investment Trends
Global private investment in generative AI showed strong growth in 2024 [1]. The U.S. expanded its lead in global AI investment in 2024 [2]. The substantial and growing investment in AI overall—and generative AI in particular—underscores the recognition of these technologies' vast potential across industries.
The U.S.'s sustained investment leadership reflects its position as a frontrunner in the AI market. The influx of funding signals strong confidence in the future of AI and generative AI. Such investments fuel further research and development, accelerating innovation and broader adoption.
Regional Differences in Public Perception and Optimism
Countries like China, Indonesia, and Thailand exhibit high optimism about AI, while Canada, the U.S., and the Netherlands show lower levels of enthusiasm [1].
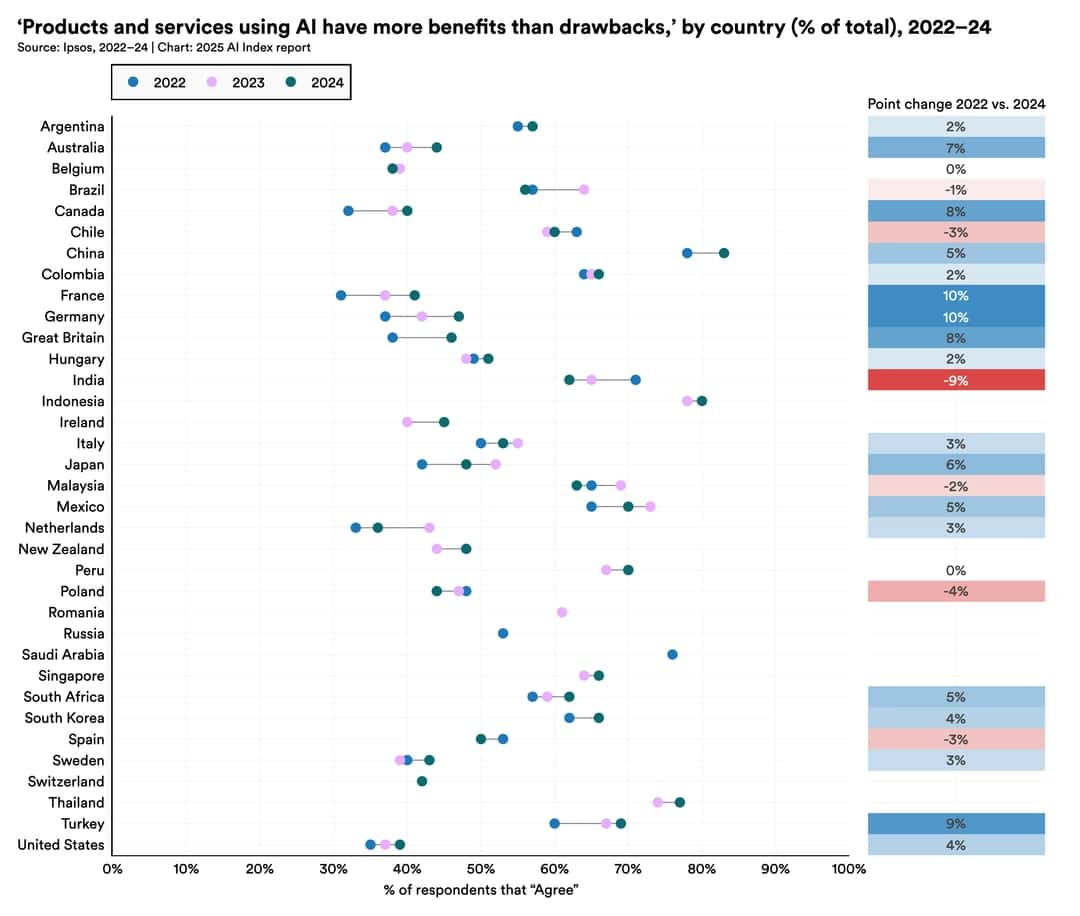
Several previously skeptical countries, including Germany, France, Canada, the U.K., and the U.S., have seen growing optimism about AI [1].
The stark regional differences in public optimism highlight varying cultural and societal perspectives on AI's benefits and risks. However, the overall rise in optimism suggests a potential global shift toward greater acceptance and understanding of AI's potential.
Higher optimism in certain regions may correlate with greater exposure to or benefits from AI technologies. The increase in optimism among previously skeptical regions indicates evolving public sentiment as AI becomes more deeply embedded in daily life.
Responsible AI and Ethical Considerations
The responsible development and deployment of AI are critical.
The Evolution of Responsible AI Ecosystems
In 2024, AI-related incidents surged, underscoring the growing need for responsible AI practices [1].
Despite the increase in incidents, standardized responsible AI (RAI) evaluations remain rare among major industrial model developers [1]. However, new benchmarks like HELM Safety, AIR-Bench, and FACTS offer promising tools for assessing AI safety and truthfulness [1].
Governments worldwide are showing heightened urgency in AI governance, with increased global collaboration, including frameworks released by organizations like the OECD and the EU [1]. The rise in AI-related incidents highlights the urgency of developing and implementing robust responsible AI frameworks. While standardized evaluations are lacking, the emergence of new benchmarks and heightened government attention indicate growing awareness and efforts to address AI's ethical challenges.
The increase in AI-related incidents serves as a stark reminder of AI's potential harms. The development of new evaluation tools and proactive government engagement suggest the field is moving toward more regulated and ethically conscious practices.
Growing Concerns About AI-Related Incidents and Harms
In 2024, AI-related incidents reached a record high, including deepfake images and chatbots linked to harmful situations [2].
These incidents underscore AI's potential for misuse and unintended negative consequences, emphasizing the importance of safety measures and ethical guidelines in AI development and deployment.
Real-world examples of AI causing harm highlight the need for preventive measures to mitigate risks. These include technical safeguards, ethical considerations, and clear guidelines for AI use.
Government and Regulatory Efforts in AI Governance
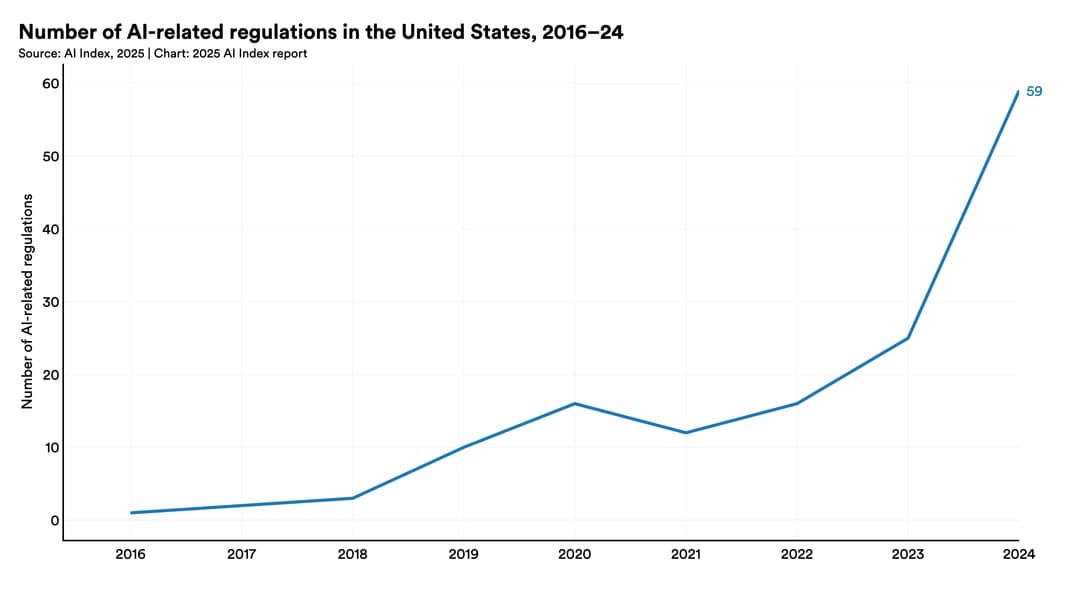
U.S. states are increasingly passing AI-related legislation, with a significant rise in such laws in 2024 [2]. Global collaboration on AI governance strengthened in 2024, with frameworks released by various international organizations [1]. The increase in legislative activity at the state and international levels reflects growing recognition of the need for governance frameworks to address AI's societal and ethical implications. This suggests a shift toward a more regulated AI ecosystem.
Governments are responding to AI's rapid advancement by establishing rules and guidelines for its development and use. This is essential to ensure responsible, safe, and equitable deployment of AI technologies.
Addressing Bias, Fairness, and Transparency in AI Systems
Mitigating bias in AI systems remains a key focus, with advances in fairness-aware machine learning algorithms and more diverse datasets [12]. Ensuring fairness and reducing bias in AI systems are critical for creating inclusive and reliable AI solutions. Ongoing research in this area reflects a commitment to addressing these ethical challenges.
Bias in training data can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes in AI applications. Efforts to develop fairness-aware algorithms and use more diverse datasets are essential for building ethical AI systems.
Future Directions and Emerging Trends
The future of AI is filled with opportunities and challenges.
The Rise of Agent AI and Its Potential Impact
Agent AI—where AI systems operate independently and collaboratively to complete tasks—is expected to have a major impact in the coming years [4].
The continued development and increasing sophistication of Agent AI systems could transform how we work, interact with technology, and solve complex problems. This trend may introduce new levels of automation and assistance across all aspects of life.
As AI agents become more capable of independent reasoning and action, they could automate complex workflows, manage tasks autonomously, and provide more proactive and personalized support.
The Convergence of AI and Robotics/Autonomous Systems
AI-powered robotics is revolutionizing supply chain management and logistics [12]. Advances in robotics, driven by AI, are enabling robots that learn faster and handle a wider range of tasks [7].

The fusion of AI and robotics is creating smarter, more versatile autonomous systems capable of performing complex tasks in environments ranging from industrial settings to everyday life.
AI provides robots with the "brains" to perceive, reason, and act in more sophisticated ways. This convergence could automate physical labor and enable new forms of human-machine interaction.
Advances in AI Hardware and Chip Technology
The generative AI chip market is projected to continue significant growth in 2025 [29]. Companies are investing in custom chips designed for specific AI tasks to optimize performance and efficiency [30]. More energy-efficient AI chips and data centers are becoming a trend [8]. Ongoing advancements in AI hardware, including specialized chips and more efficient data centers, are essential to support the growing demands of complex AI models and applications.
The focus on energy efficiency is also gaining importance. AI's increasing computational needs require more powerful and efficient hardware. Custom chips can be optimized for specific AI workloads, while energy efficiency addresses sustainability concerns.
The Growing Importance of Open-Source AI Models
The expansion of open-source AI models is a key trend for 2025, potentially lowering barriers to entry in the AI field [7].
The growth of open-source AI fosters collaboration, innovation, and broader access to AI technologies, potentially accelerating progress and democratizing AI development.
Open-source models allow researchers and developers to build on existing work, share knowledge, and contribute to collective AI advancements. This can lead to faster innovation and wider adoption of AI technologies.
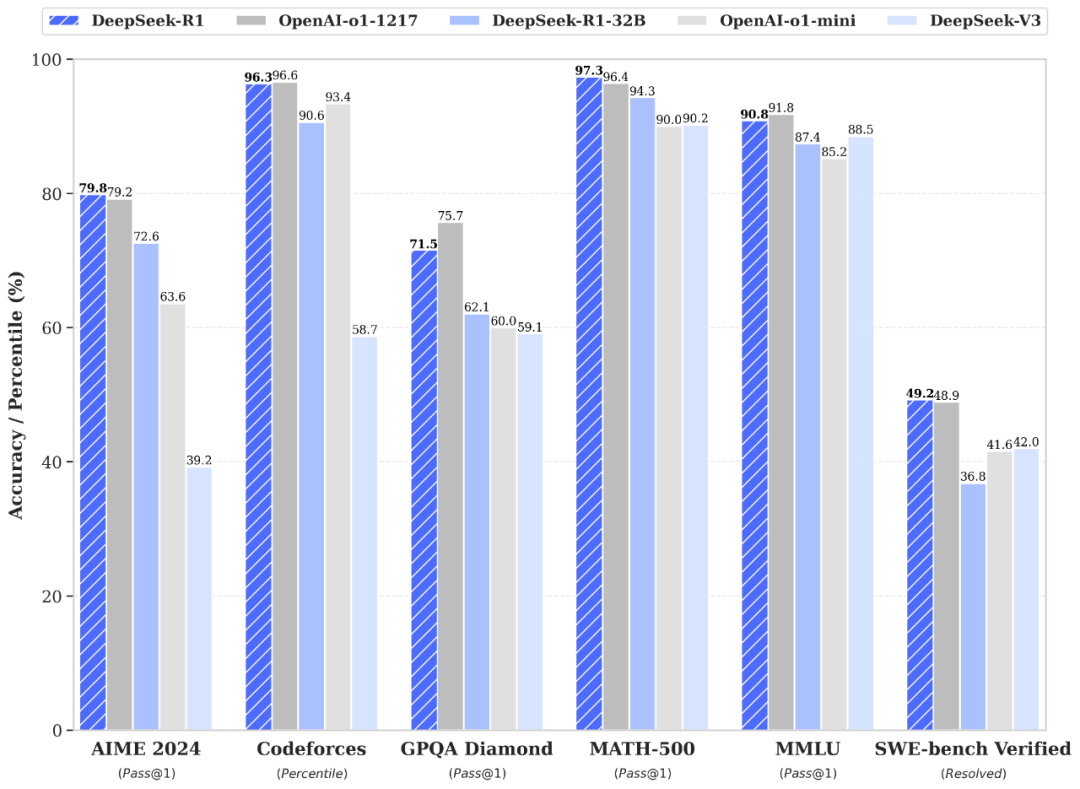
Notably, a Chinese AI startup open-sourced the DeepSeek-R1 model in early 2025, which performs on par with OpenAI's GPT-4, intensifying competition in the AI model space.
Conclusion
In 2024 and early 2025, AI made significant strides across multiple domains. Its impact is increasingly felt in industries such as healthcare, transportation, business, and education.
Global competition and collaboration in AI research and development continue to unfold. Responsible AI practices and efforts toward ethical development and governance are becoming more critical.
The continued rise of Agent AI, convergence with robotics, hardware advancements, and the role of open-source AI are key trends shaping the future.
AI's transformative potential is immense, but sustained research, ethical considerations, and responsible deployment remain essential.
Key Tables
- Table: AI Benchmark Performance Improvements
| Benchmark Name | 2023 Score (if applicable) | 2024 Score | Improvement (Percentage Points) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MMMU | Introduced in 2023 | +18.8 | 18.8 |
| GPQA | Introduced in 2023 | +48.9 | 48.9 |
| SWE-bench | Introduced in 2023 | +67.3 | 67.3 |
- Table: U.S. vs. China in AI Model Development
| Metric | United States | China |
|---|---|---|
| Notable AI Models (2024) | 40 | 15 |
| Leads in AI Publications (2024) | No | Yes |
| Leads in AI Patents (2024) | No | Yes |
| Private AI Investment (2024, $B) | 109.1 | 9.3 |
References
- The 2025 AI Index Report | Stanford HAI, accessed May 6, 2025, https://hai.stanford.edu/ai-index/2025-ai-index-report
- AI Index 2025: State of AI in 10 Charts | Stanford HAI, accessed May 6, 2025, https://hai.stanford.edu/news/ai-index-2025-state-of-ai-in-10-charts
- Artificial Intelligence Index Report 2025 - AWS, accessed May 6, 2025, https://hai-production.s3.amazonaws.com/files/hai_ai_index_report_2025.pdf
- Five Trends in AI and Data Science for 2025 - MIT Sloan Management Review, accessed May 6, 2025, https://sloanreview.mit.edu/article/five-trends-in-ai-and-data-science-for-2025/
- Critical AI Issues in Europe and Beyond - MIT Technology Review - YouTube, accessed May 6, 2025, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3eMbN7wy6VI
- Shifting Long-Context LLMs Research from Input to Output - arXiv, accessed May 6, 2025, https://arxiv.org/html/2503.04723v2
- Year in review: Google's biggest AI advancements of 2024, accessed May 6, 2025, https://blog.google/technology/ai/2024-ai-extraordinary-progress-advancement/
- 6 AI trends you'll see more of in 2025 - Microsoft News, accessed May 6, 2025, https://news.microsoft.com/source/features/ai/6-ai-trends-youll-see-more-of-in-2025/
- Introducing deep research - OpenAI, accessed May 6, 2025, https://openai.com/index/introducing-deep-research/
- OpenAI's Deep Research: A Guide With Practical Examples - DataCamp, accessed May 6, 2025, https://www.datacamp.com/blog/deep-research-openai
- Understanding complex trends with deep research | OpenAI, accessed May 6, 2025, https://openai.com/index/deep-research/
- Artificial Intelligence Breakthroughs: Key Developments to Expect in 2025 | Ironhack Blog, accessed May 6, 2025, https://www.ironhack.com/us/blog/artificial-intelligence-breakthroughs-a-look-ahead-to-2024
- The state of AI: How organizations are rewiring to capture value - McKinsey & Company, accessed May 6, 2025, https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights/the-state-of-ai
- MIT's 10 breakthrough technologies for 2025 - LEAP:IN, accessed May 6, 2025, https://www.insights.onegiantleap.com/blogs/mits-10-breakthrough-technologies-for-2025/
- The Top AI Trends for 2025 - TecEx, accessed May 6, 2025, https://tecex.com/the-top-ai-trends-for-2025/
- 54 NEW Artificial Intelligence Statistics (Apr 2025) - Exploding Topics, accessed May 6, 2025, https://explodingtopics.com/blog/ai-statistics
- AI year in review: Advancements and predictions for 2025 - Unanet, accessed May 6, 2025, https://unanet.com/blog/ai-year-in-review-advancements-and-predictions-for-2025
- AI in Financial Modeling and Forecasting: 2025 Guide - Coherent Solutions, accessed May 6, 2025, https://www.coherentsolutions.com/insights/ai-in-financial-modeling-and-forecasting
- AI in Banking: 2025 Trends - Devoteam, accessed May 6, 2025, https://www.devoteam.com/expert-view/ai-in-banking-2025-trends/
- Artificial Intelligence Applications in Finance: Real-World Success Cases for 2025, accessed May 6, 2025, https://acropolium.com/blog/artificial-intelligence-applications-in-finance-real-world-success-cases/
- Generative Artificial Intelligence in Financial Services Strategic Business Report 2025: Global Market to Grow by $16.2 Billion During 2024-2030, Expansion of AI Chatbots Creates New Opportunities - GlobeNewswire, accessed May 6, 2025, https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2025/03/19/3045626/28124/en/Generative-Artificial-Intelligence-in-Financial-Services-Strategic-Business-Report-2025-Global-Market-to-Grow-by-16-2-Billion-During-2024-2030-Expansion-of-AI-Chatbots-Creates-New-.html
- 2025 AI Trends in Financial Management - Citizens Bank, accessed May 6, 2025, https://www.citizensbank.com/corporate-finance/insights/artificial-intelligence-trends-report-2025.aspx
- AI Trends in Ed Tech to Watch in 2025 - EdTech Magazine, accessed May 6, 2025, https://edtechmagazine.com/k12/article/2025/01/ai-trends-ed-tech-watch-2025
- Main AI Trends In Education (2025) - Custom AI Agents | Springs, accessed May 6, 2025, https://springsapps.com/knowledge/main-ai-trends-in-education-2024
- 5 AI Trends Reshaping Education: Data & Applications - Number Analytics, accessed May 6, 2025, https://www.numberanalytics.com/blog/5-ai-trends-reshaping-education
- 25 AI predictions for 2025 - eSchool News, accessed May 6, 2025, https://www.eschoolnews.com/digital-learning/2025/01/02/ai-predictions-for-2025/
- Classrooms are adapting to the use of artificial intelligence, accessed May 6, 2025, https://www.apa.org/monitor/2025/01/trends-classrooms-artificial-intelligence
- AI in software engineering at Google: Progress and the path ahead, accessed May 6, 2025, https://research.google/blog/ai-in-software-engineering-at-google-progress-and-the-path-ahead/
- 2025 global semiconductor industry outlook - Deloitte, accessed May 6, 2025, https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/technology/technology-media-telecom-outlooks/semiconductor-industry-outlook.html
- 5 AI Trends Shaping Innovation and ROI in 2025 | Morgan Stanley, accessed May 6, 2025, https://www.morganstanley.com/insights/articles/ai-trends-reasoning-frontier-models-2025-tmt
- Top AI Hardware Trends Shaping 2025 - Trio Dev, accessed May 6, 2025, https://trio.dev/ai-hardware-trends/
- 31 Mar, 2025 - Aventine, accessed May 6, 2025, https://www.aventine.org/next-generation-ai-chips-gpus-nvidia/
Leave your comment
- No comments yet.
Recommended AI Tools
Carefully selected AI tools to improve your work, study, and live efficiency.
Related Articles
Standing at this moment in 2025, when we look back at the development journey of artificial intelligence, we witness how this revolutionary technology has reshaped every aspect of human society. From initial theoretical concepts to today's practical applications, each step forward in AI technology has changed the way we live. Let's revisit this fascinating journey together.
In 2024 and early 2025, the field of artificial intelligence (AI) achieved remarkable progress, with its impact spanning across various industries. AI models demonstrated significant performance improvements in multiple benchmarks, marking a new level of capability in handling complex tasks <sup>[1]</sup>. From healthcare to transportation, AI is integrating into daily life at an unprecedented pace <sup>[1]</sup>. Business adoption and investment in AI also showed strong growth, particularly in generative AI <sup>[1]</sup>. The United States maintained its lead in AI model development, but China is rapidly closing the quality gap <sup>[1]</sup>. Meanwhile, the responsible AI ecosystem continues to evolve, with increasing attention to ethical considerations and regulation <sup>[1]</sup>. Global optimism about AI has risen overall, though regional differences persist <sup>[1]</sup>.
Gemini CLI is an open-source AI agent that brings Gemini directly into your terminal, with MCP support for extensibility and Human in the Loop for oversight. Individual developers get unmatched usage limits at no cost.